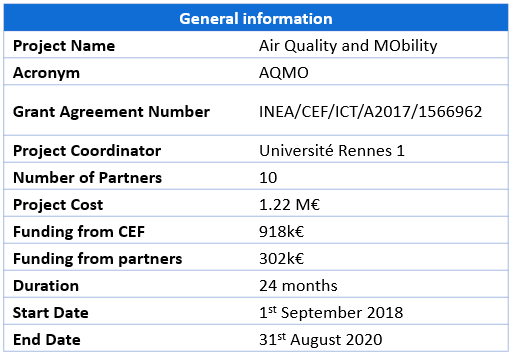
The European project Air Quality and MObility (AQMO), which started this September, gathered all its partners in Rennes, France on October 16th on the occasion of its first official meeting.
Co-financed by the European Union through its CEF programme, AQMO addresses the air quality challenge, thanks to the development of a smart city pilot in the area of Rennes Metropole. The project will provide an end-to-end urban platform that extends current practices in air quality measurements. The AQMO platform will provide citizens, local authorities, scientists and private companies with new data and innovative services based on computing simulation.
With these services, the project will provide a new type of air quality analysis for urban planification, create new economic activities and jobs and stimulate citizen involvement, and thus achieve air quality improvement.
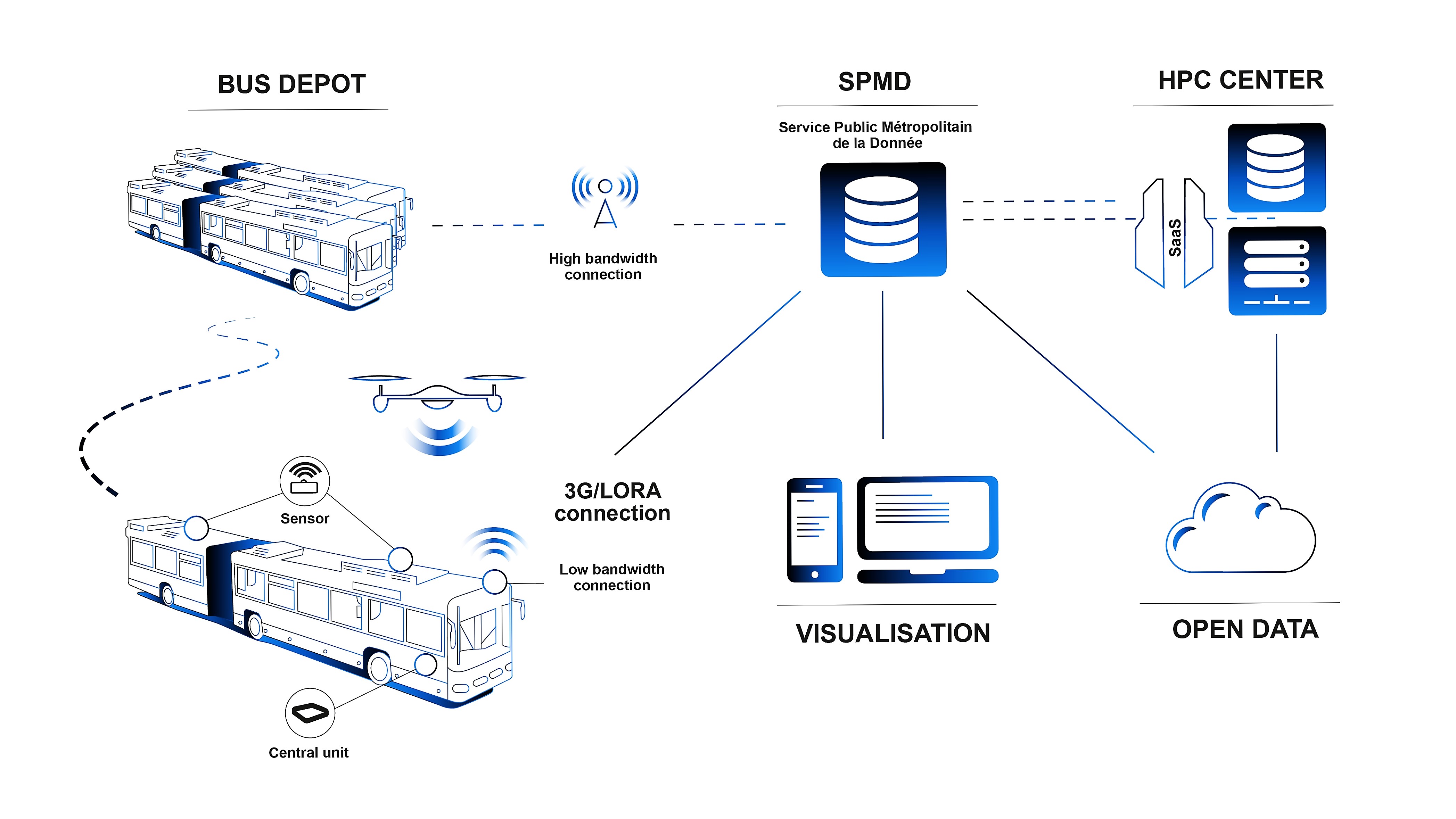
The project uses a transversal approach – spanning from micro-sensors to supercomputers – in order to deliver day-to-day data. AQMO intends to explore the use of High-Performance Computing (HPC) to create value for citizens, on one hand, and to back decision-making by public authorities on the other hand. These HPC capabilities are necessary to perform the numerical simulation with an accurate pollution dispersion model that would include sensors data-assimilation.
Thanks to the exploitation of the local transportation network (equipped with high quality mobile sensors), the project will be able to achieve rigorous air quality measurements in a wide area rather cost-effectively. This would then allow the extension of the geographical area covered and the use of more reliable and profitable sensors (e.g. drones for measurements of catastrophic events). Through the use and implementation of HPC as a service and a support to decision-making, the results will grant better understanding of pollution propagation inside the Rennes area. The data results will ultimately be made available to citizens via the SPMD (an Open-Data Metropolitan Service) that is being developed by Rennes Metropole.
Several technical challenges are addressed within the project:
- Defining a set of open-source APIs and data schemes with corresponding meta data that would take advantage of the SPMD and existing European Data Portal;Several technical challenges are addressed within the project:
- Implement efficient and cost-effective data and computing resources management;
- Measurement validation and calibration;
- Citizen data access and visualization;
- Design a sensor platform that is reliable and mobile thanks to the Rennes Metropole bus network.
The AQMO pilot is the first European attempt to provide such an end-to-end smart city platform using HPC in air quality measurement. Its methodology and approach could be extended to other cities and organizations in the future. The project will take advantage of its partners’ networks to spread its findings to scientific communities, decision makers and citizen.
To achieve its goal, the AQMO project consortium – that includes several HPC ecosystem stakeholders – gathers a large and complementary set of skills necessary to ensure a successful deployment: